Securing Your Windows Environment: A Guide to App Control for Business and Managed Installers in Microsoft Intune
In today's threat landscape, new malicious files and applications emerge daily, posing significant risks to organizational security. Microsoft Intune's App Control for Business policies provide a powerful solution for managing which applications can run on your Windows devices, helping you maintain a secure and controlled environment.
Understanding App Control for Business
App Control for Business policies are part of Intune's endpoint security capabilities, leveraging the Windows ApplicationControl Configuration Service Provider (CSP) to manage approved applications on Windows devices. This approach gives organizations granular control over their application ecosystem, ensuring that only trusted software runs on managed devices.
The core principle is simple yet effective: any applications not explicitly allowed by your policies are blocked from running. However, you also have the flexibility to deploy policies in audit mode, which allows all apps to run while logging their details for review and policy refinement.
The Power of Managed Installers
One of the most compelling features of App Control for Business is the managed installer capability. By configuring the Intune Management Extension as a managed installer, you create an automated trust framework for your application deployments.
Here's how it works: once enabled, every application you deploy through Intune is automatically tagged by the installer. These tagged applications are then recognized by your App Control for Business policies as safe, trusted apps that are allowed to run on your devices. This automation significantly reduces the administrative overhead of maintaining application control policies while maintaining robust security.
The Intune Management Extension is an Intune service that supplements Windows MDM features, facilitating the installation of Win32 apps and PowerShell scripts on managed devices. When configured as a managed installer, it uses AppLocker rules to tag applications as trusted by your organization.
Getting Started with Managed Installers
Setting up managed installers has become more flexible with recent updates. As of August 2025, Intune replaced the single tenant-wide policy with a new design that supports assignment to specific groups of devices. This means you can now:
Deploy managed installer policies to different groups of Windows devices
Use scope tags for more granular control
Target specific device groups while excluding others
The setup process is straightforward:
Navigate to Endpoint security > App Control for Business in the Microsoft Intune admin center
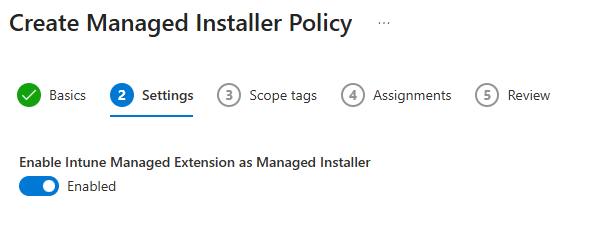
Select the Managed installer tab and create a new policy
Configure the policy to enable the Intune Managed Extension as a managed installer
4. Assign the policy to your target device groups
Once deployed, all applications subsequently installed through Intune on those devices will be automatically tagged as trusted.
Creating App Control for Business Policies
When creating an App Control for Business policy, you have two configuration options:
Built-in Controls: This is the simplest approach, allowing you to easily approve all apps installed by a managed installer and trust Windows components and store apps. You can configure additional trust options such as:
Apps with good reputation (using Microsoft Intelligent Security Graph)
Apps from managed installers
Windows components and store apps
Custom XML: For more advanced scenarios, you can provide custom XML properties that define precise control over which applications are allowed.
The built-in controls option is particularly powerful for organizations getting started with application control, as it provides robust protection without requiring deep technical knowledge of policy XML structures.
Creating App Control for Business XML Policy
Step 1: Launch Policy Creator
Open the App Control Wizard from the Start Menu
On the Welcome page, select Policy Creator
Click Next
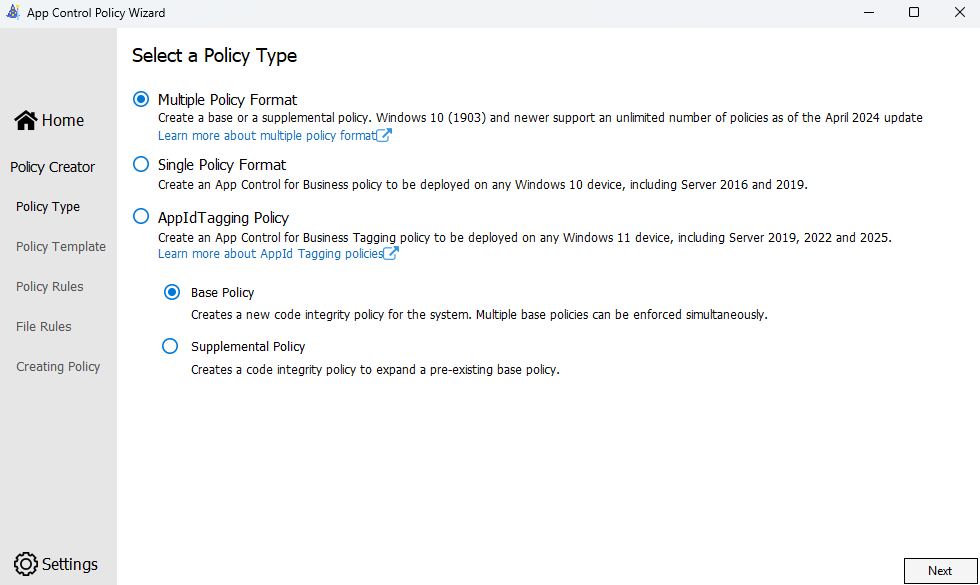
Step 2: Select Policy Type
Choose "Multiple Policy Format" and select "Base Policy". The Multiple Policy Format allows the base policy to be expanded with supplemental policies later.
Policy Type Options:
Base Policy - The primary policy that defines core trust rules
Supplemental Policy - Extends a base policy with additional rules
Click Next
Step 3: Configure Policy Details
Enter a Policy Name (descriptive name for your organization)
Choose a File Location to save the policy
Click Next
Step 4: Select a Policy Template
The wizard offers three template policies with different trust and security models, listed in order of increasing trust:
Default Windows Mode - Most restrictive, trusts only Windows components
Allow Microsoft Mode - Trusts Windows and Microsoft-signed applications
Signed and Reputable Mode - Trusts Windows, Microsoft, and applications with good reputation from the Intelligent Security Graph (ISG)
Recommendation: Start with "Signed and Reputable Mode" for most organizations, as it provides a good balance between security and usability.
Click Next
Step 5: Configure Policy Rules
By default, all templates have Audit Mode enabled. In Audit Mode, no applications are blocked—instead, the policy logs an event whenever an application outside the policy is started.
Key Policy Rules to Configure:
Audit Mode - Toggle ON for initial deployment (recommended), OFF for enforcement
Managed Installer - Enable to trust applications installed by authorized sources like Intune Management Extension
Require WHQL - Enable to allow only Windows Hardware Quality Labs signed drivers
Script Enforcement - Enable to enforce policy on PowerShell and other scripts
Allow Supplemental Policies - Enable if you plan to create supplemental policies later
Best Practice: Keep Audit Mode enabled during initial rollout to monitor impact without blocking applications.
Click Next
Step 6: Configure File Rules
File rules specify the level at which applications are identified and trusted. They are the main mechanism for defining trust in the App Control policy.
Understanding File Rule Levels
The wizard supports multiple file rule types:
Publisher Rules (Certificate-based):
Publisher - Most specific: Exact publisher, product, filename, and version
Product Name - Allows all versions of a specific product from a publisher
File Name - Allows files with specific names from a publisher
Issuing CA + Publisher - Allows all products from a publisher signed by a specific CA
Issuing CA - Allows all applications signed by certificates from a specific CA
Root CA - Broadest: Allows all applications signed by certificates in a root CA chain
Other Rule Types:
Path Rules - Allow applications in specific file system locations
Hash Rules - Allow specific files by their cryptographic hash (high maintenance)
Adding Custom Rules
Click + Custom Rules to open the custom file rule panel
Select Rule Type (Publisher, Path, Hash, or File Attributes)
For Publisher rules:
Click Browse and select a reference file signed by the desired publisher
Use the slider to select the specificity level
Check/uncheck attributes to fine-tune the rule
Click Create Rule
Repeat for all necessary custom rules
Review the Rules Table:
The left panel shows all allow and deny rules in your policy
Select any rule and click the delete button to remove it
Confirm deletions when prompted
Click Next
Step 7: Review and Save
Review the policy configuration summary
Note the output location (default: Documents folder)
Click Create Policy or Next
Output Files:
XML file (.xml) - Used for Intune deployment and policy editing
Binary file (.cip) - Used for local testing on devices
The wizard may show a "Wizard Integrity Issue" warning—you can safely ignore this and click No to proceed.
Creating App Control for Business XML Policy in Intune
Part 1: Deploying a Base Policy to Intune
Step 1: Access the Intune Admin Center
Sign in to the Microsoft Intune admin center at https://intune.microsoft.com
Navigate to Endpoint security in the left navigation menu
Select App Control for Business
Step 2: Create a New Policy
Click + Create Policy at the top of the page
In the Create a profile window:
Platform: Select Windows 10 and later
Profile: Select App Control for Business
Click Create
Step 3: Configure Basics
Enter a Name for your policy (e.g., "App Control for Business XML")
Enter a Description (optional but recommended):
Step 4: Configure Settings
In the Configuration settings page:
Configuration settings format: Select XML data
This is the only option available and correct for custom policies
Application control policy:
Click Browse (folder icon)
Navigate to your policy XML file (e.g.,
MyBasePolicy.xml)Select the file and click Open
The filename will appear in the field
Click Next
Step 5: Add Scope Tags (Optional)
If your organization uses scope tags for role-based access control:
Click Select scope tags
Choose the appropriate scope tags
Click Select
Click Next
If you don't use scope tags, simply click Next
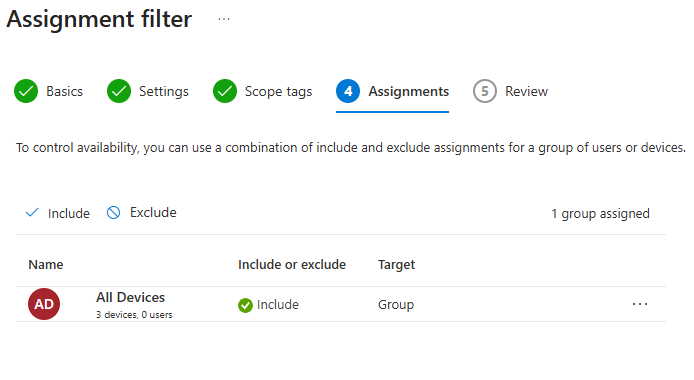
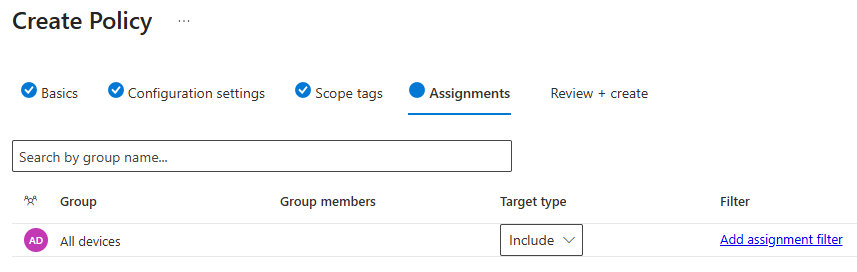
Step 6: Assign to Device Groups
IMPORTANT: Start with a pilot group, not all devices!
Under Included groups, click + Add groups
Search for and select your pilot device group (e.g., "Pilot - App Control Testing")
Click Select
Click Next
Step 7: Review and Create
Review all settings:
Policy name and description
XML file name
Assigned groups
Click Create
The policy is now created and will begin deploying to assigned devices.
Expanding Control with Supplemental Policies
Base policies establish your core application trust framework, but supplemental policies allow you to expand that trust circle for specific groups or scenarios. For example:
Create a base policy for your entire organization that trusts Windows components and managed installer apps
Add a supplemental policy for your executive team that allows additional business-critical applications
Deploy another supplemental policy for your IT help desk with tools specific to their needs
This flexibility ensures that you can maintain security while accommodating the diverse application needs across your organization.
Important Considerations
Timing Matters: Applications deployed before enabling the managed installer won't be retroactively tagged. If you're implementing App Control for Business in an existing environment, consider starting with audit mode to identify untagged applications and create appropriate policies to allow them.
Device Requirements: App Control for Business policies support Windows 10 (version 1903 or later) and Windows 11 on Enterprise, Education, and Professional editions. Azure Virtual Desktop and co-managed devices are also supported with proper configuration.
Education Tenants: For educational organizations, Windows 11 SE devices receive automatic WDAC policy and managed installer configuration, optimized for classroom environments.
Monitoring and Management
Intune provides comprehensive reporting capabilities for both App Control for Business and managed installer policies. You can monitor:
Device and user check-in status
Device assignment status
Per-setting status showing success, error, and conflict counts
Historical trends for device status
These insights help you identify and resolve issues quickly, ensuring your application control policies remain effective.
Best Practices
Start Early: Configure the Intune Management Extension as a managed installer at your next available opportunity to ensure all future app deployments are properly tagged.
Use Audit Mode First: When implementing App Control for Business in existing environments, deploy policies in audit mode initially to understand your application landscape before enforcing restrictions.
Leverage Advanced Hunting: Use Microsoft Defender for Endpoint's Advanced Hunting feature to query audit events across your managed devices and craft more effective policies.
Plan for Hybrid Environments: If you have Microsoft Entra hybrid-join devices, ensure they have connectivity to on-premises domain controllers during provisioning to successfully apply managed installer policies.
Conclusion
App Control for Business with managed installers represents a significant step forward in Windows application security. By combining automated trust tagging with flexible policy controls, organizations can maintain a secure environment without sacrificing productivity or creating excessive administrative burden.
Whether you're just beginning your application control journey or looking to enhance existing security measures, Intune's App Control for Business provides the tools you need to protect your Windows devices from unwanted and malicious applications.